Lunar vs. Solar Eclipse: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Sun and Moon’s Greatest Shows
Have you ever wondered about the fantastical dance between the Sun, Moon, and Earth that creates such breathtaking spectacles? This article will take you on a captivating journey, exploring how lunar eclipses and solar eclipses occur, the roles these celestial bodies play, and the stunning visual displays they produce. We’ll also delve into the rich tapestry of cultural significance and historical beliefs surrounding these events. And for the aspiring astronomer or curious onlooker, youll find essential tips on observing and photographing these awe-inspiring phenomena. Buckle up; you’re about to dive deep into the cosmos!
Key Takeaways
- Lunar eclipses occur when the Earth blocks sunlight from hitting the Moon.
- Solar eclipses happen when the Moon blocks sunlight from hitting the Earth.
- Lunar eclipses are safe to watch directly without special equipment.
- Solar eclipses require special glasses for safe viewing.
- Lunar eclipses are more common and easier to see than solar eclipses.

How Lunar Eclipses Occur
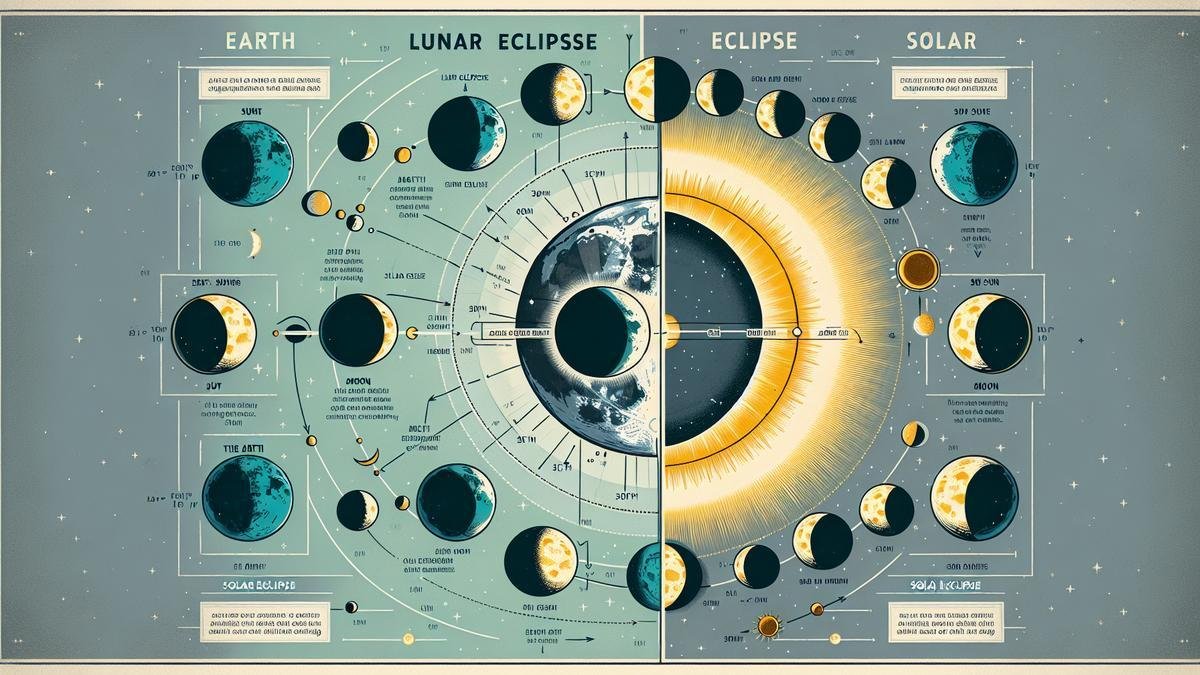
Lunar eclipses are some of the most fascinating celestial events you can witness. They occur when the Earth comes directly between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. This cosmic alignment creates a breathtaking spectacle that has intrigued humans for centuries.
The Role of the Earths Shadow
The Earth’s shadow plays a crucial role in a lunar eclipse. When the Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, it blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon. This shadow consists of two parts: the umbra and the penumbra. The umbra is the central, darkest part of the shadow, while the penumbra is the outer, lighter part.
During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon passes through the umbra, resulting in a dramatic darkening of the Moon’s surface. In a partial lunar eclipse, only a portion of the Moon enters the umbra, creating a partial shadow. A penumbral lunar eclipse, on the other hand, occurs when the Moon passes through the penumbra, causing a subtle shading on the Moon’s surface.
Phases of a Lunar Eclipse
Lunar eclipses unfold in distinct phases, each offering a unique view of the event. Here are the key phases you should watch for:
- Penumbral Eclipse Begins: The Moon enters the Earth’s penumbra, causing a slight dimming that is often hard to notice.
- Partial Eclipse Begins: The Moon starts to move into the Earth’s umbra, creating a noticeable shadow on the Moon’s surface.
- Total Eclipse Begins: The entire Moon is now within the umbra, giving it a reddish hue known as the “Blood Moon.”
- Maximum Eclipse: The peak of the eclipse, where the Moon is closest to the center of the umbra.
- Total Eclipse Ends: The Moon begins to exit the umbra, and the reddish color starts to fade.
- Partial Eclipse Ends: The Moon completely leaves the umbra, with only the penumbral shadow remaining.
- Penumbral Eclipse Ends: The Moon exits the penumbra, and the eclipse is over.
Best Times to Watch
The best times to watch a lunar eclipse depend on your location and the timing of the event. Lunar eclipses are visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth. Unlike solar eclipses, you don’t need any special equipment to view a lunar eclipse—just your eyes and a clear sky.
To enhance your experience, consider using a telescope or binoculars. These tools can provide a closer look at the Moon’s surface and the shadow’s progression. If you’re interested in photographing the eclipse, check out some techniques for photographing solar eclipses that can also be applied to lunar eclipses.
Now, let’s delve into the fascinating world of solar eclipses and explore how they differ from their lunar counterparts.
How Solar Eclipses Occur
Solar eclipses are equally mesmerizing but occur under different circumstances. They happen when the Moon moves between the Sun and the Earth, casting a shadow on the Earth. This alignment can result in a total, partial, or annular solar eclipse, each offering a spectacular show.
The Role of the Moons Shadow
The Moon’s shadow is the key player in a solar eclipse. Unlike a lunar eclipse, where the Earth’s shadow is cast on the Moon, a solar eclipse involves the Moon casting its shadow on the Earth. This shadow has two main parts: the umbra and the penumbra.
- Umbra: The central, darkest part of the shadow where the Sun is completely obscured.
- Penumbra: The outer, lighter part of the shadow where the Sun is only partially obscured.
During a total solar eclipse, the Moon’s umbra sweeps across the Earth’s surface, creating a path of totality where the Sun is entirely covered. In a partial solar eclipse, only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is too far from the Earth to completely cover the Sun, resulting in a “ring of fire” effect.
Phases of a Solar Eclipse
Solar eclipses also occur in distinct phases, each offering a unique view of the event. Here are the key phases to watch for:
- First Contact: The Moon begins to move in front of the Sun, marking the start of the eclipse.
- Second Contact: The Moon covers the Sun completely, leading to totality in a total solar eclipse.
- Maximum Eclipse: The peak of the eclipse, where the Sun is most obscured.
- Third Contact: The Moon starts to move away from the Sun, ending totality.
- Fourth Contact: The Moon completely exits the Sun’s disk, and the eclipse is over.
Best Times to Watch
Observing a solar eclipse requires careful planning. Unlike lunar eclipses, solar eclipses are only visible from specific locations on Earth, depending on the path of the Moon’s shadow. It’s essential to be in the right place at the right time to experience the full spectacle.
Safety is paramount when observing a solar eclipse. Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection, such as eclipse glasses or a solar filter for your telescope. For tips on capturing stunning images of a solar eclipse, you might find this guide on techniques for photographing solar eclipses helpful.
Comparing Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Now that you understand how lunar and solar eclipses occur, let’s compare these two celestial phenomena in more detail.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Lunar Eclipse | Solar Eclipse |
|---|---|---|
| Occurrence | Earth between Sun and Moon | Moon between Sun and Earth |
| Visibility | Visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth | Visible only from specific locations on Earth |
| Safety | Safe to view with the naked eye | Requires special eye protection |
| Frequency | More frequent (2-4 times a year) | Less frequent (2-5 times a year) |
| Duration | Can last several hours | Usually lasts only a few minutes |
| Cultural Significance | Often associated with omens and myths | Historically seen as significant and sometimes ominous |
Visual Differences
The visual experience of a lunar eclipse is quite different from that of a solar eclipse. During a lunar eclipse, you’ll see the Moon gradually darken and turn a reddish hue as it passes through the Earth’s shadow. This phenomenon is often called a “Blood Moon” due to its eerie, reddish appearance.
In contrast, a solar eclipse involves the Sun being partially or completely obscured by the Moon. During a total solar eclipse, the sky darkens, stars become visible, and the Sun’s corona—a halo of plasma—can be seen around the Moon. An annular solar eclipse creates a stunning “ring of fire” effect.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Both lunar and solar eclipses have held significant cultural and historical importance throughout human history. Ancient civilizations often viewed eclipses as omens or messages from the gods. For example, the ancient Chinese believed that a solar eclipse was caused by a dragon devouring the Sun, while the Inca associated lunar eclipses with a jaguar attacking the Moon.
In modern times, eclipses continue to captivate our imagination and inspire scientific inquiry. They provide valuable opportunities for astronomers to study celestial mechanics and the properties of the Sun and Moon.
How Solar Eclipses Happen
Solar eclipses are one of nature’s most spectacular events. Imagine standing outside and seeing the Sun slowly being covered by the Moon, casting an eerie shadow over the Earth. This phenomenon occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Earth and the Sun, blocking out the Sun’s light. But how exactly does this happen? Let’s dive deeper into the mechanics of solar eclipses.
The Moons Position
The Moon orbits the Earth in an elliptical path, which means its distance from the Earth varies. For a solar eclipse to occur, the Moon must be in the new moon phase, where it is positioned directly between the Earth and the Sun. However, this alignment alone isn’t enough. The Moon’s orbit is tilted about 5 degrees relative to the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. This tilt means that during most new moons, the Moon passes above or below the Sun. Only when the orbits intersect at points called nodes can a solar eclipse take place.
Types of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses come in three main types, each offering a different visual experience:
- Total Solar Eclipse: This occurs when the Moon completely covers the Sun, casting a shadow on the Earth and turning day into night for a short period. The path of totality, where the total eclipse is visible, is typically narrow, spanning about 100 miles wide. Outside this path, you may see a partial eclipse.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: Here, only a portion of the Sun is obscured by the Moon. This type of eclipse is more common and can be seen over a larger area. The Sun looks like it has a bite taken out of it.
- Annular Solar Eclipse: This happens when the Moon is too far from the Earth to completely cover the Sun. Instead, a ring of the Sun, known as the “ring of fire,” remains visible around the Moon. This type of eclipse is also known as a “ring eclipse.”
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between these types:
| Type of Eclipse | Description | Visibility Area |
|---|---|---|
| Total Solar Eclipse | Moon completely covers the Sun | Narrow path of totality |
| Partial Solar Eclipse | Part of the Sun is obscured by the Moon | Larger area |
| Annular Solar Eclipse | Moon covers the center of the Sun, leaving a ring | Moderate area |

Cultural Significance of Eclipses
Eclipses have fascinated humanity for millennia. They are more than just celestial events; they are cultural phenomena that have inspired myths, legends, and celebrations across different civilizations.
Historical Beliefs
Imagine standing in ancient times, watching the sky darken as the Moon covers the Sun or the Earth’s shadow creeps over the Moon. For many ancient cultures, these events were awe-inspiring and often terrifying. They didn’t have the scientific understanding we do today, so they turned to stories and beliefs to explain these phenomena.
Ancient Civilizations and Eclipses
In ancient China, a solar eclipse was thought to be caused by a celestial dragon devouring the Sun. People would bang pots and drums to scare the dragon away. Similarly, the Vikings believed that wolves Sköll and Hati chased the Sun and Moon, causing eclipses when they caught their prey.
The Mayans, known for their advanced astronomical knowledge, saw eclipses as significant but dangerous events. They believed that an eclipse was a time when the gods demanded sacrifices to ensure the continuation of the world.
Religious Interpretations
Eclipses also held religious significance. In Hindu mythology, the demon Rahu is said to swallow the Sun or Moon, causing an eclipse. This is why during an eclipse, many Hindus refrain from eating or drinking, believing that the event pollutes food and water.
In Christianity, eclipses have been interpreted as omens. The Bible mentions eclipses in the context of divine judgment and significant events. For example, the crucifixion of Jesus is said to have been accompanied by a solar eclipse.
Modern-Day Celebrations
Fast forward to today, and eclipses are often celebrated rather than feared. With our advanced understanding of astronomy, we can predict eclipses with incredible accuracy, turning them into opportunities for communal gatherings and scientific observation.
Viewing Parties and Festivals
During major solar and lunar eclipses, people gather for viewing parties, often equipped with telescopes, cameras, and special glasses. These events can feel like a mix between a scientific expedition and a festival. In some places, schools and museums organize educational events to teach people about the science behind eclipses.
In the United States, the 2017 total solar eclipse, dubbed the “Great American Eclipse,” saw millions of people traveling to the path of totality. Towns and cities along the path hosted festivals, concerts, and other events to celebrate the occasion.
Cultural Events and Traditions
In some cultures, traditional practices are still observed. For instance, in India, people take ritual baths in holy rivers during an eclipse, believing it purifies the body and soul. In Japan, some people still practice ancient rituals to ward off evil spirits during an eclipse.
Eclipses in Folklore
Folklore from around the world is rich with stories about eclipses, each offering a unique perspective on these celestial events.
Native American Legends
For many Native American tribes, eclipses were seen as a time of renewal and reflection. The Navajo, for example, believe that an eclipse is a time when the Sun and Moon are having a conversation. They see it as a period to stay indoors, avoid looking at the sky, and reflect on one’s life.
African Myths
In some African cultures, eclipses were seen as a time of conflict between celestial beings. The Batammaliba people of Togo and Benin believe that the Sun and Moon are fighting during an eclipse. They see it as a time to resolve conflicts among people, promoting peace and reconciliation.
European Folktales
European folklore often depicted eclipses as ominous events. In medieval Europe, a solar eclipse was sometimes seen as a sign of an impending disaster. People would pray and perform rituals to protect themselves from the perceived dangers.
Understanding the Differences Between Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Now that we’ve explored the cultural significance of eclipses, let’s dive into the scientific aspects and understand the differences between lunar and solar eclipses.
How Each Type of Eclipse Occurs
Both types of eclipses involve the Sun, Earth, and Moon, but they occur in different ways.
Solar Eclipses
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, casting a shadow on the Earth. This can only occur during a new moon. There are three types of solar eclipses:
- Total Solar Eclipse: The Moon completely covers the Sun, casting a shadow on Earth and turning day into night for a short period.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: Only a part of the Sun is obscured by the Moon.
- Annular Solar Eclipse: The Moon is too far from Earth to completely cover the Sun, resulting in a ring of sunlight around the Moon.
Lunar Eclipses
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. This can only happen during a full moon. There are three types of lunar eclipses:
- Total Lunar Eclipse: The Earths shadow completely covers the Moon, often giving it a reddish color due to the scattering of sunlight through the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: Only a part of the Moon enters the Earths shadow.
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: The Moon passes through the Earths penumbral shadow, causing a subtle dimming.
Roles of the Sun, Earth, and Moon
The positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon are crucial in determining the type of eclipse.
| Eclipse Type | Sun Position | Earth Position | Moon Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Eclipse | Fixed | Orbiting the Sun | Between Sun and Earth |
| Lunar Eclipse | Fixed | Between Sun and Moon | Orbiting Earth |
Why They Result in Different Phenomena
The key differences in solar and lunar eclipses lie in their visibility and the visual effects they produce.
Solar Eclipse Phenomena
- Day Turns to Night: During a total solar eclipse, the sky darkens as if it were night.
- Solar Corona: The Suns corona, or outer atmosphere, becomes visible, creating a stunning halo effect.
- Temperature Drop: A noticeable drop in temperature can occur due to the sudden lack of sunlight.
Lunar Eclipse Phenomena
- Red Moon: During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon often appears red, a phenomenon known as a “Blood Moon.”
- Extended Duration: Lunar eclipses can last for several hours, offering more time to observe the event.
- Visibility: Unlike solar eclipses, which are visible only in specific areas, lunar eclipses can be seen from anywhere on the night side of the Earth.
Occurrence and Visibility
Eclipses don’t happen every month due to the tilt of the Moon’s orbit relative to the Earths orbit around the Sun.
Frequency of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses are relatively rare events for any given location on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs approximately every 18 months somewhere on Earth, but any specific location might only experience a total eclipse once every 360 to 410 years.
Frequency of Lunar Eclipses
Lunar eclipses are more frequent and can occur up to three times a year. They are visible from anywhere on the night side of the Earth, making them more accessible to a larger audience.
Tips for Observing and Photographing Eclipses
Observing and photographing eclipses can be a thrilling experience. Here are some tips to help you make the most of these celestial events.
Observing Solar Eclipses
- Safety First: Never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection. Use eclipse glasses or a solar viewer.
- Best Locations: Find a location within the path of totality for a total solar eclipse. Check eclipse maps to plan your viewing spot.
- Equipment: Use a telescope with a solar filter for a closer view. A pair of binoculars with solar filters can also enhance your experience.
Observing Lunar Eclipses
- No Special Equipment Needed: You can observe a lunar eclipse with the naked eye, although binoculars or a telescope can enhance the view.
- Best Viewing Conditions: Find a dark location away from city lights for the best experience. Clear skies are crucial, so check the weather forecast.
Photographing Eclipses
- Solar Eclipses: Use a DSLR or mirrorless camera with a telephoto lens. A solar filter is essential to protect your cameras sensor. Check out techniques for photographing solar eclipses for more tips.
- Lunar Eclipses: A tripod and a camera with manual settings are ideal. Use a long exposure to capture the details of the Moon. For enhancing your photos, consider using Lightroom for astrophotography.
Interesting Facts About Eclipses
Here are some fascinating tidbits about eclipses that you might not know.
Solar Eclipses
- Baily’s Beads: Just before and after totality, the rugged lunar landscape allows beads of sunlight to shine through in some places and not in others, creating a phenomenon known as Baily’s Beads.
- Diamond Ring Effect: As the total eclipse ends, a single bright spot of sunlight shines through, resembling a diamond ring.
- Eclipse Chasers: Some people travel around the world to witness solar eclipses, planning their trips years in advance.
Lunar Eclipses
- Super Blood Moon: When a total lunar eclipse coincides with a supermoon, the event is called a “Super Blood Moon,” making it even more spectacular.
- Saros Cycle: Eclipses occur in cycles known as the Saros cycle, which lasts approximately 18 years, 11 days, and 8 hours. Eclipses separated by one Saros cycle share similar geometry.
Tips for Observing Eclipses
Essential Gear for Viewing
When you’re gearing up to witness one of nature’s most spectacular events, having the right equipment can make all the difference. Let’s dive into the essential gear you’ll need for both lunar and solar eclipses.
Solar Eclipse Viewing Gear
- Eclipse Glasses: These are a must. Regular sunglasses won’t protect your eyes from the Sun’s harmful rays. Eclipse glasses are specially designed to filter out the intense light.
- Solar Filters for Telescopes: If you plan to use a telescope, ensure it has a solar filter. This will protect your eyes and your equipment.
- Pinhole Projector: A simple and safe way to view a solar eclipse. You can make one with just a piece of cardboard and aluminum foil.
- Solar Viewing Binoculars: These are equipped with special filters to protect your eyes while giving you a closer look at the eclipse.
Lunar Eclipse Viewing Gear
- Binoculars: While you can see a lunar eclipse with the naked eye, binoculars will give you a more detailed view.
- Telescope: For an even closer look, a telescope is ideal. It will allow you to see the surface of the Moon in great detail.
- Camera with a Tripod: Capturing the moment can be magical. A camera on a tripod will help you take steady, clear photos.
Ideal Locations for Eclipse Watching
Finding the perfect spot to watch an eclipse can enhance your experience. Here are some tips on where to go.
Solar Eclipse Locations
- Path of Totality: For a total solar eclipse, you need to be in the path of totality. This is a narrow path where the moon completely covers the Sun.
- Open Fields: Avoid areas with tall buildings or trees that can block your view.
- High Altitudes: Mountains or high hills can provide a clearer view, free from atmospheric distortions.
Lunar Eclipse Locations
- Dark Skies: The darker the sky, the better. Rural areas far from city lights are ideal.
- High Ground: Like solar eclipses, higher altitudes can offer a clearer view.
- Wide Open Spaces: Ensure you have a clear horizon view, as the Moon will be low in the sky at the beginning or end of the eclipse.
Photography Tips
Capturing the beauty of an eclipse can be challenging but rewarding. Here are some tips to help you get the perfect shot.
Solar Eclipse Photography
- Use a Solar Filter: Never point your camera directly at the Sun without a solar filter. This can damage your camera and your eyes.
- Tripod: A tripod is essential for keeping your camera steady.
- Remote Shutter Release: This will help you avoid camera shake when taking photos.
- Adjust Settings: Use a low ISO and a fast shutter speed to avoid overexposure.
Lunar Eclipse Photography
- Long Exposure: Since lunar eclipses happen at night, you’ll need a long exposure to capture enough light.
- Manual Focus: Autofocus can struggle in low light, so switch to manual focus for sharper images.
- Experiment with Settings: Start with a high ISO and a slow shutter speed, then adjust as needed.
For more detailed techniques on photographing solar eclipses, check out this comprehensive guide on techniques for photographing solar eclipses.
Understanding the Differences Between Lunar and Solar Eclipses
Eclipses are awe-inspiring events that have fascinated humans for centuries. But what exactly are the differences between lunar and solar eclipses? Let’s break it down.
How Each Type of Eclipse Occurs
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking out the Sun’s light. There are three types of solar eclipses:
- Total Solar Eclipse: The Moon completely covers the Sun, casting a shadow on Earth.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: Only part of the Sun is covered by the Moon.
- Annular Solar Eclipse: The Moon covers the center of the Sun, leaving a ring-like appearance.
Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. There are three types of lunar eclipses:
- Total Lunar Eclipse: The entire Moon enters Earth’s umbra (the central, darkest part of its shadow).
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: Only a part of the Moon enters Earth’s umbra.
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: The Moon passes through Earth’s penumbra, causing a subtle shading.
Roles of the Sun, Earth, and Moon
In both types of eclipses, the Sun, Earth, and Moon play crucial roles. Here’s a table to illustrate their positions:
| Eclipse Type | Sun Position | Earth Position | Moon Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Eclipse | Stationary | Stationary | Between Sun and Earth |
| Lunar Eclipse | Stationary | Between Sun and Moon | Stationary |
Visual Phenomena
The visual experience of each type of eclipse is vastly different.
Solar Eclipse
- Day Turns to Night: During a total solar eclipse, the sky darkens as if it’s nighttime.
- Corona: The Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona, becomes visible.
- Baily’s Beads: Bright spots of light that appear as the Moon covers the Sun.
Lunar Eclipse
- Red Moon: During a total lunar eclipse, the Moon often turns a reddish color, known as a “Blood Moon.”
- Gradual Change: The eclipse progresses slowly, allowing for extended observation.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Eclipses have held significant cultural and historical importance across various civilizations.
Solar Eclipse
- Ancient Omens: Many ancient cultures viewed solar eclipses as omens or messages from the gods.
- Scientific Discoveries: The study of solar eclipses has led to significant scientific discoveries, including the confirmation of Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
Lunar Eclipse
- Myths and Legends: Lunar eclipses have been the source of many myths and legends, often seen as a time of change or transformation.
- Cultural Celebrations: Some cultures celebrate lunar eclipses with rituals and ceremonies.
Occurrence and Visibility
The frequency and visibility of eclipses vary.
Solar Eclipse
- Rarity: Total solar eclipses are rare, occurring about once every 18 months.
- Visibility: Only visible from a narrow path on Earth’s surface.
Lunar Eclipse
- Frequency: Lunar eclipses are more common, occurring at least twice a year.
- Visibility: Visible from anywhere on the night side of Earth.
Impact on Human Observation
Eclipses have a profound impact on human observation and scientific study.
Solar Eclipse
- Scientific Research: Solar eclipses provide a unique opportunity to study the Sun’s corona and other phenomena.
- Public Interest: Solar eclipses often attract large crowds and media attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a lunar eclipse?
A lunar eclipse happens when Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.
What causes a solar eclipse?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun’s light.
How often do lunar and solar eclipses happen?
Lunar eclipses can happen about twice a year. Solar eclipses occur around two to five times a year but each location on Earth might see one every 18 months or so.
Why are lunar eclipses visible from more places than solar eclipses?
During a lunar eclipse, anyone on the night side of Earth can see it. In contrast, a solar eclipse’s shadow is much smaller, making it visible only from certain spots.
Are solar eclipses safe to watch?
No, never look directly at a solar eclipse without special glasses. Watching it unprotected can harm your eyes. Lunar eclipses are safe to watch with the naked eye.